55503004
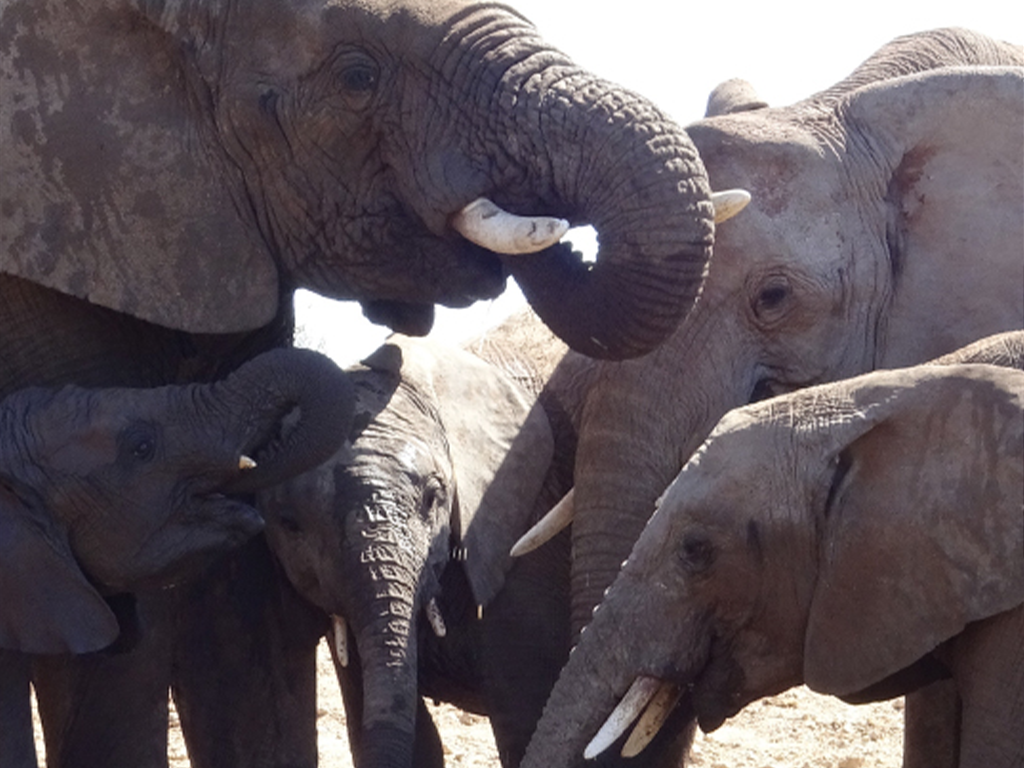
Tiere in Afrika
In 10 interaktiven Aufgaben und Videos wird Wissen zu den Tieren in Afrika vermittelt und abgefragt.
Das Medium bietet H5P-Aufgaben an, die ohne zusätzliche Software verwendbar sind.
Durch interaktive Aufgabentypen wird das audiovisuelle und interaktive Lernen einfach.
Lernen macht jetzt Spaß!
Included Tasks
- I Afrikas wilde Tiere – Interaktive Aufgabe mit Video
- II Afrikas große Raubkatzen: Der Löwe – Interaktive Aufgabe mit Video
- III Der Leopard – Interaktive Aufgabe mit Video
- IV Der Gepard – Interaktives Video
- V Warum ist der Gepard so schnell? – Bildkarten
- VI Hundeartige: Schakale
- VII Wildhunde – Interaktive Aufgabe mit Video
- VIII Nahrungsopportunisten: Hyäne
- IX Krokodil – Interaktive Aufgabe mit Video
- X Pflanzenfresser – Interaktive Aufgabe mit Video
- XI Beute oder Jäger – Interaktive Aufgabe
- XII Aggression im Tierreich – Interaktive Aufgabe
Curriculum-centred and oriented towards educational standards
Matching
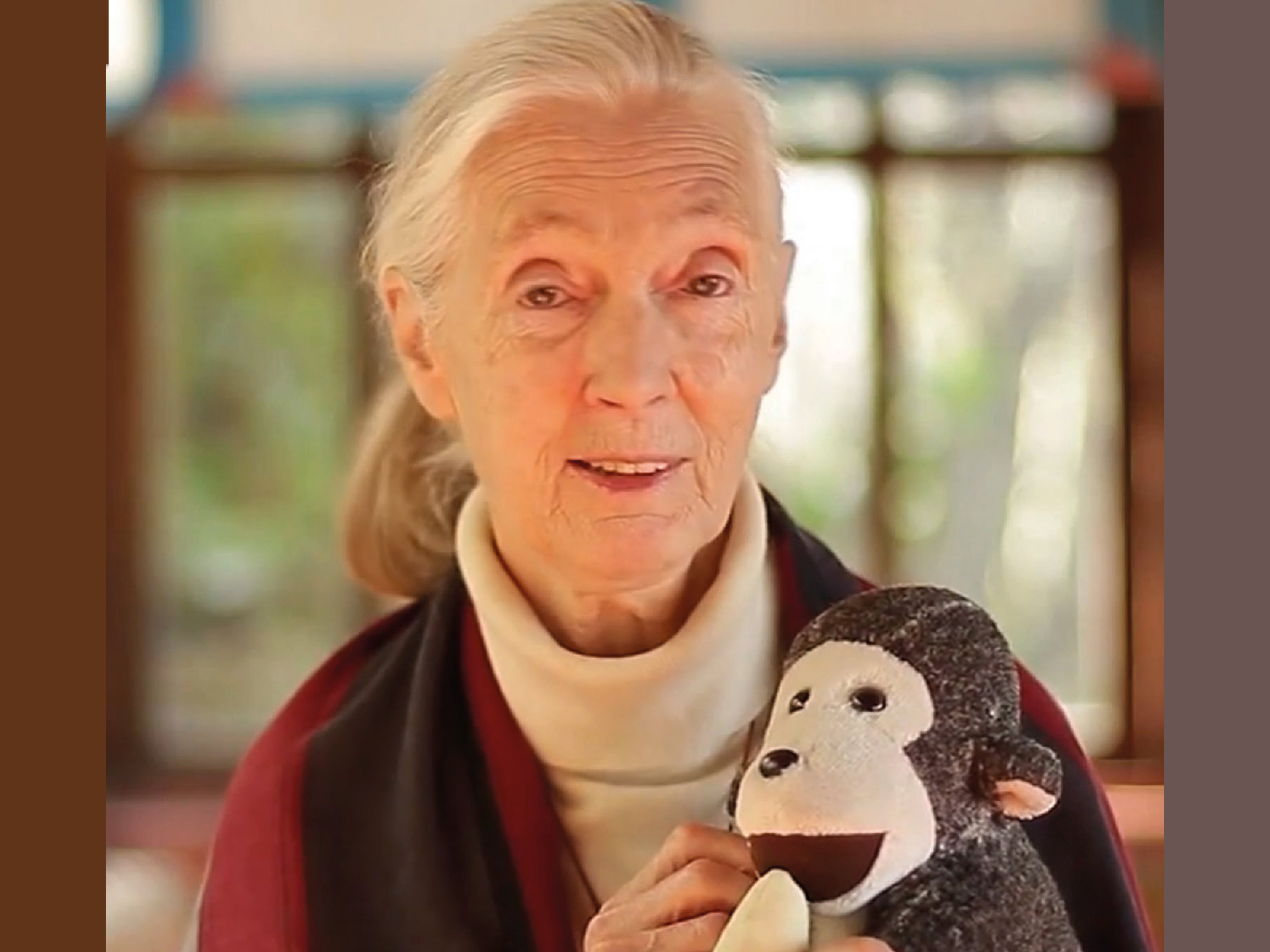
Jane Goodall
Jane Goodall is considered a pioneer among behavioral scientists in the world of chimpanzees. At the age of only 26, she began her work as a scientist in Tanzania, East Africa, in early 1960. She lives with free-ranging chimpanzees and provides insights into their social behavior and abilities. As founder of the Jane Goodall Institute, she has worked since 1986 to raise awareness and sustainability regarding the coexistence of humans, animals and the environment. The film provides insights into the life and work of Jane Goodall.
Single-cell Organisms
The Earth is the only planet known to us where liquid water ─ the source of life ─ exists.